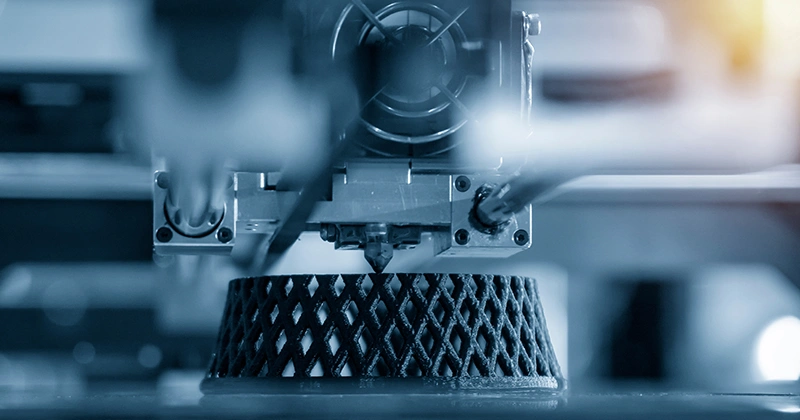
The production principle of 3D printing technology
SLA 3D printing
SLA 3D printing (stereolithography modeling technology) uses ultraviolet laser to polymerize on the surface of liquid thermosetting photosensitive resin to draw thousands of thin layers to form a three-dimensional solid molding method. Wide selection of materials, extremely high feature resolution and high-quality surface treatment are options for SLA 3D printing.
SLS 3D printing
SLS 3D printing (stereoscopic laser sintering technology) uses high-power optical lasers under computer control to sinter the solid part of the powder according to the interface contour information, and then continuously circulates and builds up layers to produce complex and durable geometric parts. SLS 3D printing builds strong parts from filled nylon material, suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
FDM 3D printing
FDM 3D printing (fused lamination molding technology) uses high temperature to melt the material, extrude it through the print head to form filaments, and accumulate and shape it on the component platform. FDM is the simplest and most common 3D printing technology, usually applied to desktop 3D printing equipment.

 Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Español
Español